This post is protected. To view it, enter the password below!
Protected: Emergenze ematologiche: identificazione e trattamento
di Dr. Darrell Edward Jones, dr.ssa Jennifer J. Walker, dr. Alain Michael P. Abellada • April 2025
Le emergenze ematologiche comprendono disturbi emorragici o della coagulazione, sia ereditari sia acquisiti, che richiedono un
trattamento urgente per prevenire gravi morbidità o mortalità. I pazienti che ne sono colpiti possono presentare emorragie spontanee,
ittero, petecchie o porpora. Gli esami diagnostici iniziali includono l’emocromo completo. Nei casi in cui l’emorragia sia legata a un
disturbo ereditario, è necessario sostituire il fattore della coagulazione deficitario prima di procedere con ulteriori accertamenti.
La sindrome toracica acuta rappresenta una complicanza poco comune, ma potenzialmente fatale, della malattia falciforme. L’emolisi
causata da patologie autoimmuni o da danni iatrogeni, ad esempio relativi a trasfusioni di emoderivati, si presenta con un quadro
clinico ben definito e richiede un intervento immediato. La trombocitopenia grave, dovuta a porpora trombocitopenica idiopatica
o a porpora trombotica trombocitopenica, richiede una corretta identificazione e un trattamento mirato. La coagulazione intravascolare
disseminata e la coagulopatia indotta da trauma possono essere talvolta confuse tra loro, ma entrambe sono in grado di provocare
conseguenze severe e richiedono terapie specifiche. Infine, è fondamentale che i medici di medicina generale sappiano riconoscere
prontamente i casi da riferire con urgenza a uno specialista ematologo.
(Am Fam Physician. 2024; 110(1):58-64. Copyright © 2024 American Academy of Family Physicians).
(Am Fam Physician. 2024; 110(1):58-64. Copyright © 2024 American Academy of Family Physicians).
Related Articles
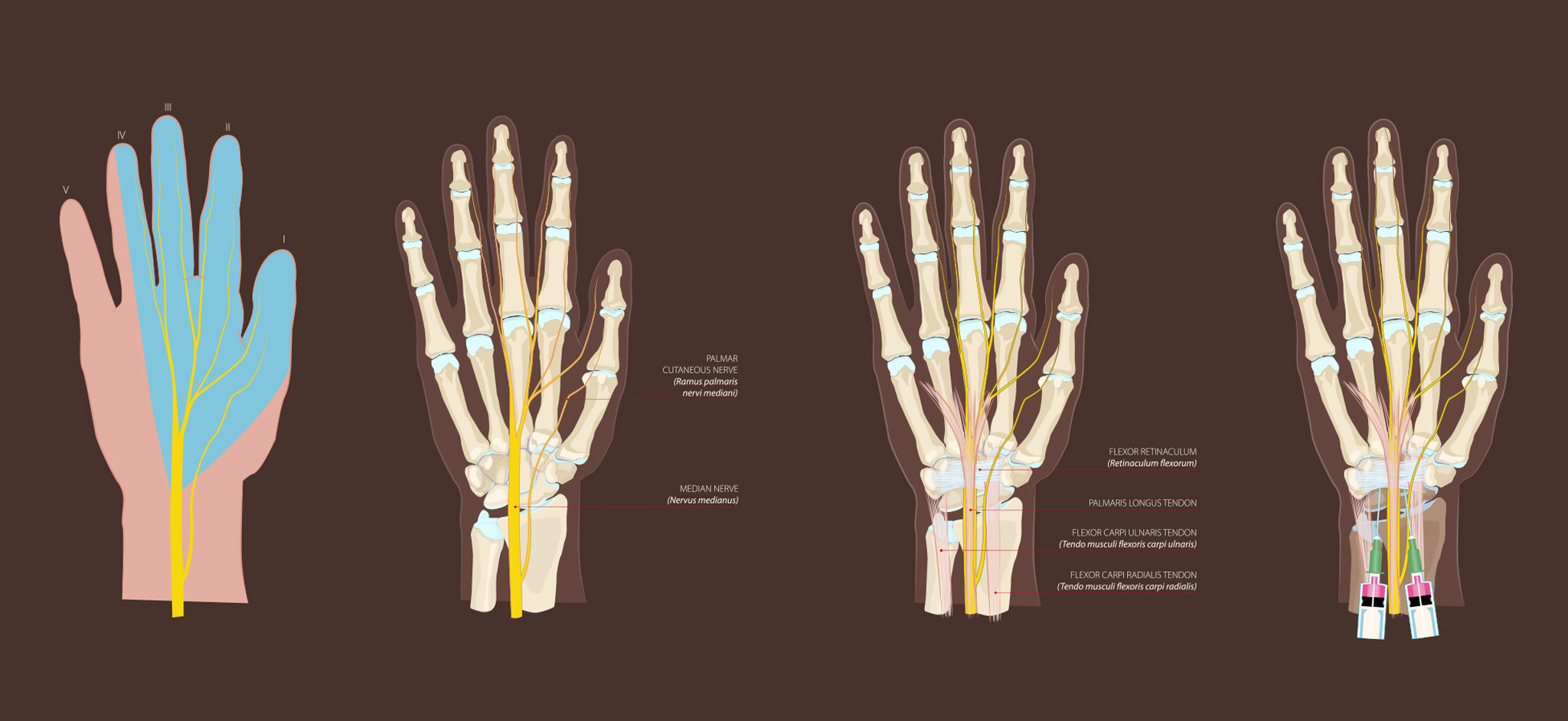
Infiltrazioni della mano e polso: Parte II. Sindrome del tunnel carpale, cisti gangliari, sindrome da intersezione, lesione del complesso fibrocartilagineo triangolare e tenosinovite di De Quervain
di
Dr. George G. A. Pujalte, Dr. Rock Vomer, Dr. Neil Shah
April 2025
Highlights
di
Aaron Saguil, Matthew V. Fargo
∙
February 2021